Since ancient times, humans have turned to nature for well-being solutions. Medicinal plants have become an invaluable resource for health, comfort, and balance.
Today, pursuing health and well-being plays a central role in society, and medicinal plants are emerging as essential allies. Beyond just remedies, they represent a unique synergy of nutrients and active compounds that strengthen bodily systems, optimising essential functions such as digestion, circulation, and immunity.
But what exactly are medicinal plants, and how can they benefit your business? How do they work, and why are they gaining such relevance in today’s market? In this article, we answer these questions and explore key aspects that will help you add value to your product range.
What Are Medicinal Plants?
Medicinal plants contain natural compounds, known as active principles, that have a therapeutic effect on the human body. Depending on the species, these principles can be found in different parts of the plant, such as leaves, flowers, roots, seeds, or bark.
Recognised for their properties, they support overall well-being by balancing the body and mind, enhancing functions like nutrient absorption, and strengthening key systems such as the immune and nervous systems.
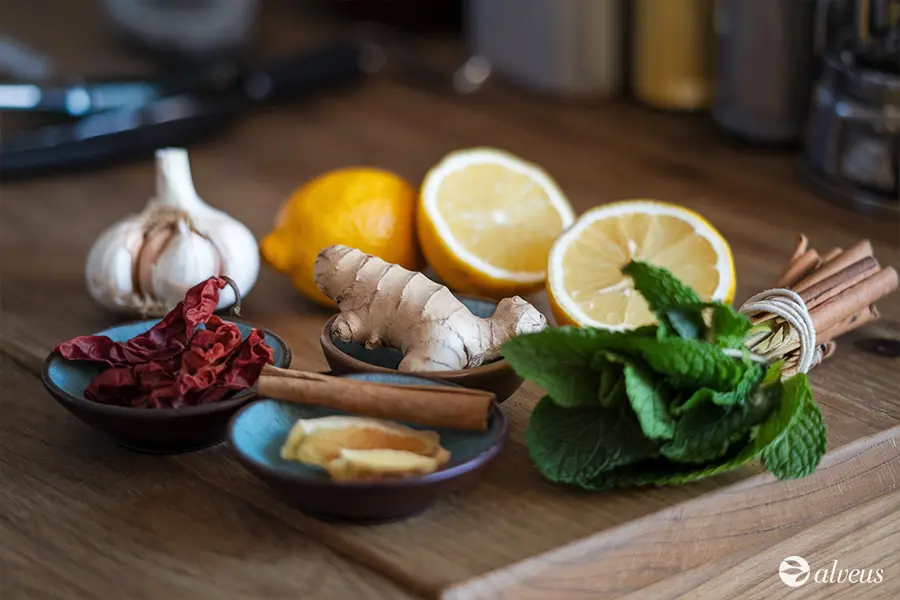

What sets medicinal plants apart is their chemical complexity: each plant contains a variety of substances that work in synergy. This combination of active principles enhances their effectiveness and makes them a natural and well-tolerated option for the body.
However, it is crucial to remember that natural does not always mean safe. Proper dosage, appropriate combinations, and in-depth knowledge are essential to fully harness their benefits responsibly.
The History and Evolution of Medicinal Plants
The relationship between humans and medicinal plants dates back to prehistoric times. Archaeological remains found at the Shanidar IV site (Iraq) suggest that Neanderthals used them in funeral rituals.
Ancient civilisations such as the Egyptians, Chinese, and Greeks documented the use of plants in written records, influencing modern herbal medicine. The De Materia Medica, written by Dioscorides in the 1st century, detailed more than 600 plants with therapeutic uses.
This natural remedy was so effective that it transformed medicine at the time, becoming a key treatment against malaria.
In recent decades, the use of medicinal plants has surged due to their effectiveness and the growing demand for natural alternatives. When used appropriately, they rarely cause severe side effects, making them a less invasive option for many individuals.
Additionally, many modern medicines are derived from plant-based active principles, such as aspirin, which originates from willow bark’s salicylic acid, or quinine, extracted from cinchona bark, used in malaria treatment.
How Do Medicinal Plants Work?
These principles can have diverse properties, such as anti-inflammatory, relaxing, digestive, and diuretic effects, depending on the plant and its composition.
In general, active principles interact with the body’s systems to trigger processes that improve health or relieve discomfort.
The method of consumption directly influences how medicinal plants and their compounds act. For instance, in an infusion like chamomile tea, the hot water extracts soluble active principles such as flavonoids, alkaloids, and tannins, which are absorbed by the body when consumed. In topical applications, such as creams or ointments, active principles penetrate the skin to treat localised issues like inflammation or wounds.
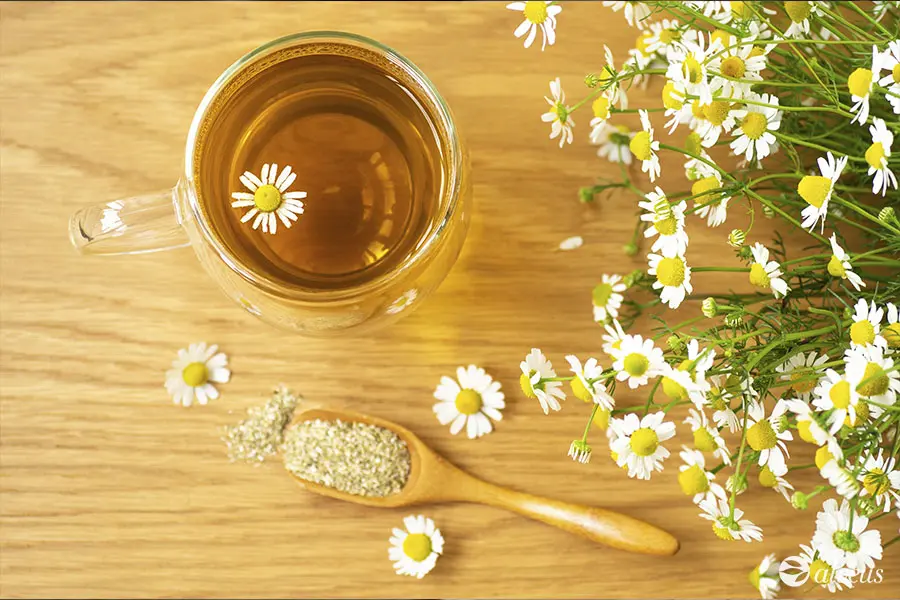

Each plant has a unique combination of active principles, making it suitable for specific conditions. For example, mint and fennel support the digestive system, while valerian and lavender have a calming effect on the nervous system.
It is important to highlight that the quality of medicinal plants and their processing is crucial to preserving their effectiveness. Factors such as harvesting, drying, and storage can affect the concentration of their active principles. Therefore, properly treated plants ensure optimal and safe results.
What Benefits Do Medicinal Plants Offer?
Here are some of the most common benefits medicinal plants can provide:
Antioxidant Properties
Plants like green tea and rosemary neutralise free radicals, reducing cellular damage and slowing ageing.
Calming and Relaxing Effects
Valerian, lemon balm, and mistletoe contain compounds that act on the nervous system, promoting relaxation, improving sleep, and reducing stress.
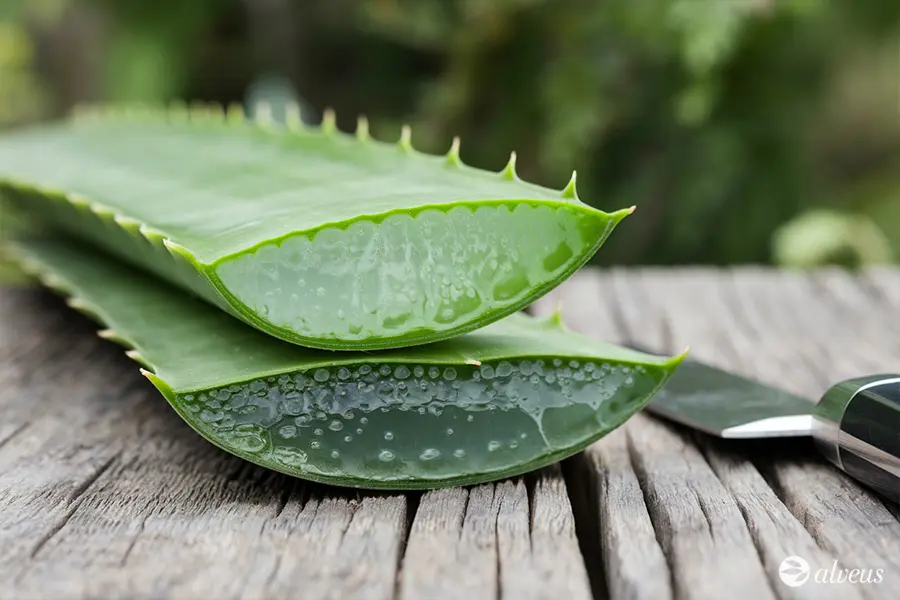
Skin Regeneration and Care
Calendula and aloe vera are examples of medicinal plants with regenerative and soothing properties that benefit the skin. Their active compounds help treat irritations, promote healing, and maintain a healthy appearance.

Digestive Support
Herbs like ginger, cardamom, and calamus root relieve digestive discomfort such as bloating and gas, stimulate digestion, and promote nutrient absorption.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Some medicinal plants, such as white willow and turmeric, contain compounds linked to reducing inflammation and relieving muscle or joint pain.
Improved Circulation and Cardiovascular Health
Plants like ginkgo biloba promote efficient blood flow and protect the cardiovascular system. Others, like chilli pepper, stimulate circulation to the extremities and may help reduce blood pressure.
Immune System Support
Plants such as echinacea and pau d’arco are known for boosting the body’s defences, helping prevent infections, and enhancing recovery from illnesses.
Conclusion
Medicinal plants are valuable resources for improving health and reflect the deep historical relationship between humans and nature.
Understanding what they are and the benefits they offer is the first step in integrating them consciously and effectively into products that benefit your customers. However, responsible use is essential.
With the right knowledge and a responsible approach, medicinal plants can become a powerful and safe tool for offering natural solutions that promote well-being.
Stay tuned as we continue exploring the fascinating world of medicinal plants. Discover how Alveus can help you curate the perfect selection tailored to your customers’ needs.